
Considering pendulums, their practical value is apparent since they are used as parts of clocks, metronomes, and seismometers. Calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon. For example, the power of gravity allows artificial satellites to orbit around Earth without falling as their mass is calculated regarding acceleration due to gravity. If materials of different weights, size, or shape had been used in the performed lab exercise, the results would still be the same because the physical force of gravity is constant for all falling objects.Īnother significant aspect of this lab exercise is that it was not merely an academic exercise because the concept of acceleration due to gravity is highly applicable in practice.
where h is the height of the fall and t is the average time of fall. This opens a broad class of interesting situations to us. Calculate the earths acceleration due to gravity using the relation (derived from calculus) g 2h / t 2. The acceleration due to gravity is constant, which means we can apply the kinematics equations to any falling object where air resistance and friction are negligible. He also performed experiments with spheres rolling down inclined planes. The mathematician and physicist Galileo Galilei defined the concept of acceleration, the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. As acceleration due to gravity is the physical constant, it does not matter what shape and size are the falling objects (any other thing could be used instead of the paper strip), and thus both methods give the same result, despite that the input data differs. The acceleration of free-falling objects is therefore called the acceleration due to gravity. THEORY The purpose of this experiment is to measure the acceleration of a freely falling object. In this lab you will be using Atwood’s Machine to measure the acceleration due to.

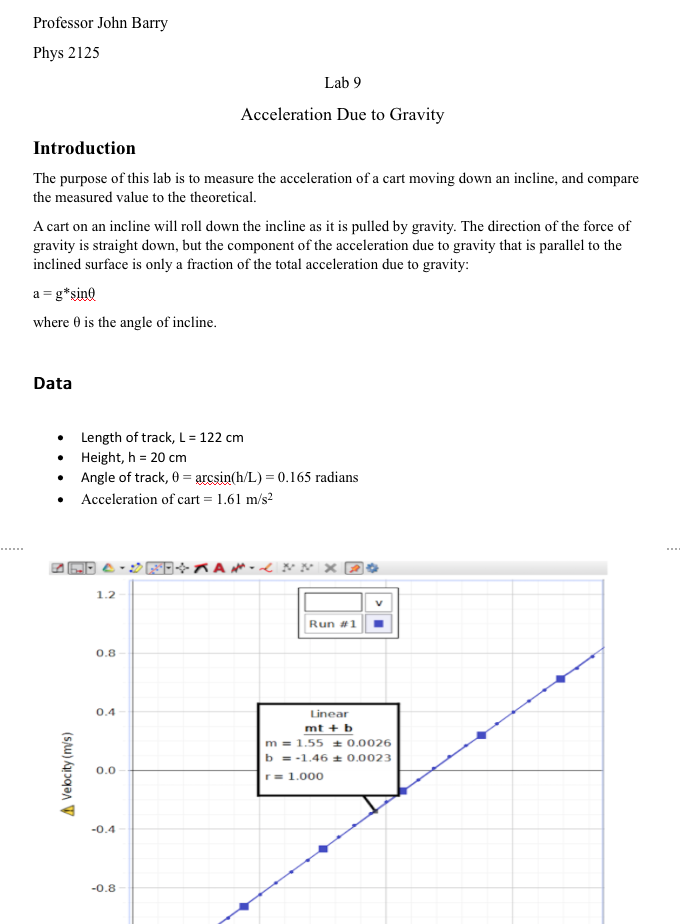
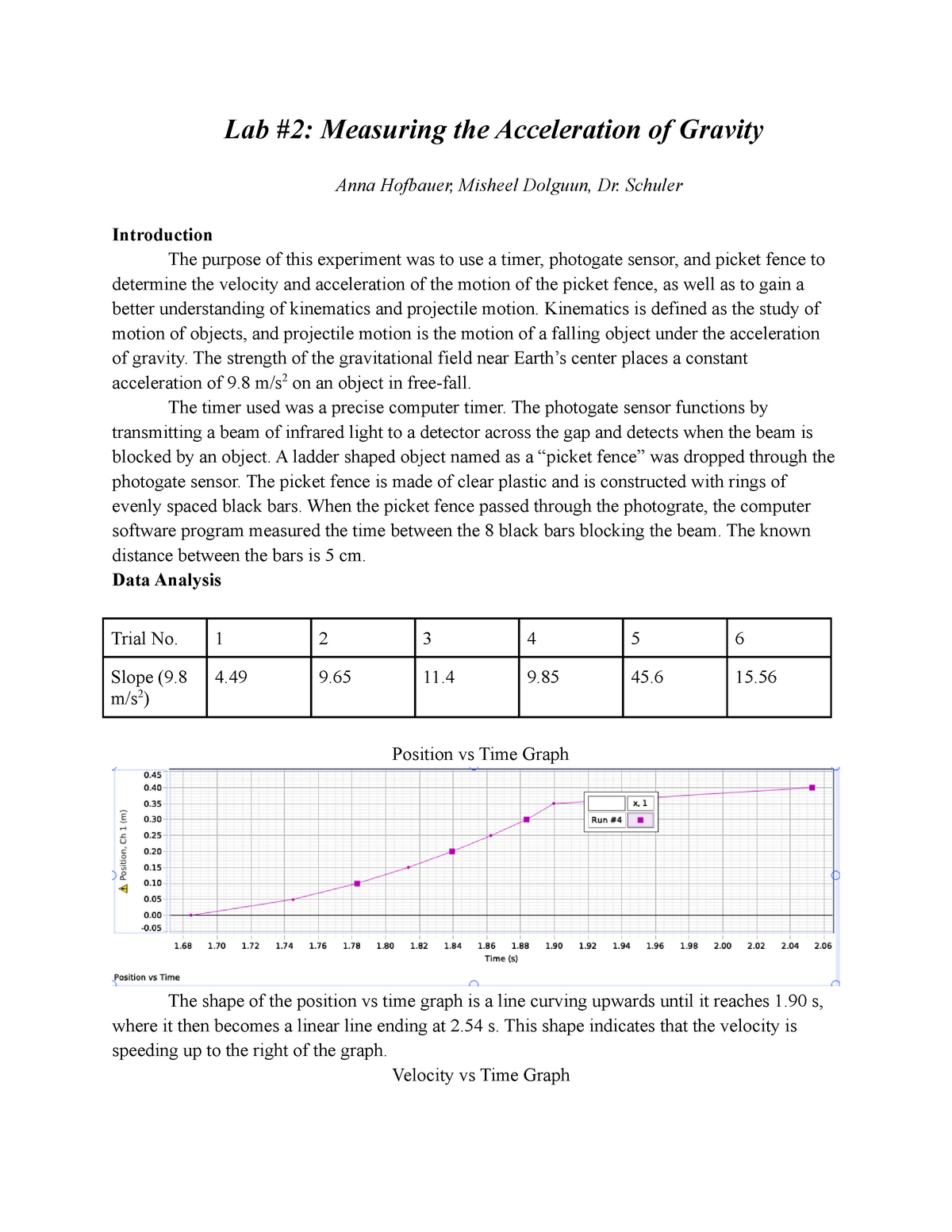
It is also highly important to emphasize why the same quantity derived from two different activities. Acceleration Due to Gravity Watch the prelab video for Lab 2 (20.53 min). Measured acceleration due to gravity: 9.53 m/s2 Accepted value of acceleration due to gravity: 9.8 m/s2 Percent difference: 2.76 Conclusion: The measured value of the acceleration due to gravity was only 2.76 lower than the commonly accepted value of 9.8 m/s2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
